The effects of estrogen therapy on menopausal women have been studied for some time, but in the last few years, there has been a host of research on the effect of estrogen on men seeking to imitate women. This research have been published in reputable medical journals.
Estrogen and Depression
Excess estrogen in the serum in natal males has been associated with depression – studies both among adult men and adolescent boys.
Increased estrogen level can be associated with depression in males
Stanikova et al, Psychoneuroendocrinology Volume 87, January 2018, Pages 196-203
Testosterone, estradiol, DHEA and cortisol in relation to anxiety and depression scores in adolescents Chronister et al, Journal of Affective Disorders, Volume 294, 1 November 2021, Pages 838-846
Clinical studies (i.e., studies that recruit actual subjects rather than rely on anonymous, online, non-probability surveys) that promote gender medicine fail to show any improvement in psychosocial outcomes among AMAB, e.g., the NEJM study.
Psychosocial Functioning in Transgender Youth after 2 Years of Hormones Chen et al,
https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2206297
In the main text, the study finds no improvement in depression, anxiety symptoms, or life satisfaction among natal male youth
http://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2206297
Why estrogen causes depression: 12 mths of estrogen treatment among trans women decreased serum BDNF levels . Decrease in BDNF is associated with increased risks of developing major depressive disorder https://t.co/BpNydUzwAV.doi.org/10.1016/j.euro…
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2014.11.019

Brain Damage
Physiologically, recent research shows that estrogen has far more serious effects.
In male rats, estrogen changed the brain to resemble those in brains of men seeking to imitate women. It reduces the water content in the astrocytes, shrinking cortical structures and increasing ventricular volume, which has been observed in other studies among men seeking to imitate women.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2020.104839
Why is that important? Astrocytes control the glutamate (a neurotransmitter) released at the synapses. They optimize neuronal functions and prevent “glutamate excitotoxicity” – a prolonged or exacerbated activation of glutamate receptors
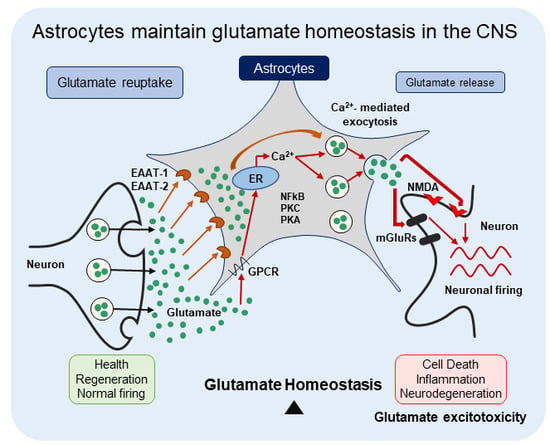
Astrocytes Maintain Glutamate Homeostasis in the CNS by Controlling the Balance between Glutamate Uptake and ReleaseGlutamate is one of the most prevalent neurotransmitters released by excitatory neurons in the central nervous system (CNS); however, residual glutamate in the extracellular space is, potentially, neu…https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8020184
Glutamate excitotoxicity can start “a cascade of neurotoxicity,” leading to the loss of neuronal function and cell death, which then leads to neurodegenerative diseases .
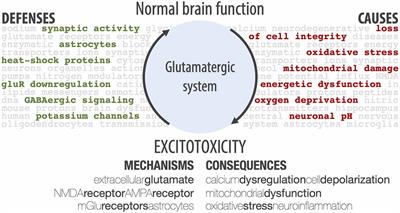
Going the Extra (Synaptic) Mile: Excitotoxicity as the Road Toward Neurodegenerative DiseasesExcitotoxicity is a phenomenon that describes the toxic actions of excitatory neurotransmitters, primarily glutamate, where the exacerbated or prolonged activation of glutamate receptors starts a casc…https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2020.00090
What does that mean? It turns out that an increase in glutamate in the brain can lead to neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s, ALS, Parkinson’s, MS, and fibromyalgia.

Glutamate: What It Is & Functionhttp://bit.ly/44DSxMo
The subcortical changes (decrease in cortical thickness and volume and increase in ventricular structures) brought about by estrogen therapy mentioned above have been linked to many neurological disorders.
Decreasing brain cortical thickness and volume is associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder and lower levels of general intelligence
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.102131
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intell.2013.07.010
The rodent study found that estrogen treatment reduced white matter integrity, which is associated with cognitive instability. And a reduction in gray matter is a prominent feature of Alzheimer’s.
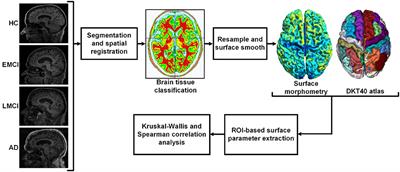
Gray Matter Deterioration Pattern During Alzheimer’s Disease Progression: A Regions-of-Interest Based Surface Morphometry StudyAccurate detection of the regions of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) lesions is critical for early intervention to effectively slow down the progression of the disease. Although gray matter volumetric abnorm…https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2021.593898
The increase in the volume of ventricular structures compresses the brain from within, eventually damaging and destroying brain tissue.
http://www.aans.org/Patients/Neurosurgical-Conditions-and-Treatments/Adult-Onset-Hydrocephalus
Reduction in hippocampal volume is associated with cognitive dysfunction and is a core symptom in patients with major depression.
RISK OF DEMENTIA
Estrogen was once believed to be a promising treatment among older menopausal women to delay onset of dementia. The WHIMS study (1996) was designed to test whether HRT reduces incidence of dementia in women 65+.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0197-2456(98)00038-5
The WHIMS study was discontinued in 2002 as it showed that long-term estrogen-progestin therapy increased the risk of dementia in women aged 65+, leading the researchers to conclude that the risks of HRT outweigh the benefits .
https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.289.20.2651
Now, a new nationwide study from Denmark among menopausal women on estrogen therapy found that it was associated with dementia, even with short-term use (the risks increased with the duration of use), and also among women younger than 65.

Menopausal hormone therapy and dementia: nationwide, nested case-control studyObjectives To assess the association between use of menopausal hormone therapy and development of dementia according to type of hormone treatment, duration of use, and age at usage. Design Nationwide…https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2022-072770
In the Danish study, MRI scans of the brain found evidence of brain atrophy, which is associated with cognitive decline and dementia . So, two studies associate estrogen therapy with dementia among natal women for its *prescribed* use.
https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2482070938
AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE
Recent research shows that estrogen therapy among trans women has been implicated in various autoimmune diseases, from MS to rheumatoid arthritis and many others (remember that an increase in glutamate is also associated with MS)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2021.10.004
INCREASED CANCER RISK
Estrogen increases the risks of prostate cancer and breast cancer among natal men. doi.org/10.1586/eem.11…
https://doi.org/10.1586/eem.11.20
https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.59.1602
Increased risk of heart disease
Among men seeking to imitate women, estrogen increases risks of cardiovascular diseases (two separate studies), often by as much as tenfold compared to women.
https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038584
In Summary
Validating the abovementioned research, empirically, we see a much higher incidence of many of these physical () and neurological diseases in the trans population.
Christina N. Dragon, Paul Guerino, Erin Ewald, and Alison M. Laffan. Transgender Medicare Beneficiaries and Chronic Conditions: Exploring Fee-for-Service Claims Data. LGBT Health. Dec 2017.404-411.http://doi.org/10.1089/lgbt.2016.0208
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annepidem.2019.09.009
Not coincidentally, perhaps, population cohort studies (two separate studies) show that men seeking to imitate women, on average, die decades earlier than either men or women.
https://doi.org/10.1215/00703370-9942002
https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00185-6
• • •

